Anaconda is a package manager, an environment manager, and Python distribution that contains a collection of many open source packages. An installation of Anaconda comes with many packages such as numpy, scikit-learn, scipy, and pandas preinstalled and is also the recommended way to install Jupyter Notebooks. This tutorial will include:
With that, let’s get started

Graphical Installation of Anaconda
Installing Anaconda using a graphical installer is probably the easiest way to install Anaconda.
1 ‒ Go to the Anaconda Website and choose a Python 3.x graphical installer (A) or a Python 2.x graphical installer (B). If you aren’t sure which Python version you want to install, choose Python 3. Do not choose both.
2 - Locate your download and double click it.
3 - Click on Continue
4 - Click on Continue
(1.b) Make Anaconda your default python installation. For data science, Anaconda rules. Ideally, when you’re in Terminal and you type python, you’d like for the Anaconda python installation to be the default python that starts running instead of what comes installed by default on a typical Macbook. Download Anaconda for Mac & read reviews. Eliminate devops. Anaconda for Mac. As a free and open-source distribution of Python and R programming language, it. For most Unix systems, you must download and compile the source code. The same source code archive can also be used to build the Windows and Mac versions, and is the starting point for ports to all other platforms. Download the latest Python 3 and Python 2 source.
5 - Note that when you install Anaconda, it modifies your bash profile with either anaconda3 or anaconda2 depending on what Python version you choose. This can important for later. Click on Continue.
6 - Click on Continue to get the License Agreement to appear.
You will need to read and click Agree to the license agreement before clicking on Continue again.
7 - Click on Install
8 - You’ll be prompted to give your password, which is usually the one that you also use to unlock your Mac when you start it up. After you enter your password, click on Install Software.
9 - Click on Continue. You can install Microsoft Visual Studio Code if you like, but it is not required. It is an Integrated Development Environment. You can learn about Python Integrated Development Environments here.
10 - You should get a screen saying the installation has completed. Close the installer and move it to the trash.
Test your Installation
1 - Open a new terminal on your Mac. You can do this by clicking on the Spotlight magnifying glass at the top right of the screen, type “terminal” then click on the terminal icon. Now, type the following command into your terminal
If you had chosen a Python 3 version of Anaconda (like the one in the image above), you will get an output similar to above.
If you had chosen a Python 2 version of Anaconda, you should get a similar output to the one below.
2 - Another good way to test your installation is to try and open a Jupyter Notebook. You can type the command below in your terminal to open a Jupyter Notebook. If the command fails, chances are that Anaconda isn’t in your path. See the next section on Common Issues.
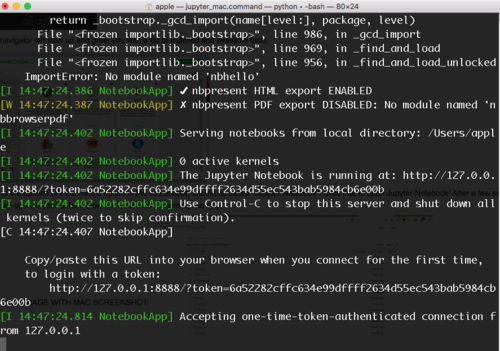
The image below shows a Jupyter Notebook in action. Jupyter notebooks contain both code and rich text elements, such as figures, links, and equations. You can learn more about Jupyter Notebooks here.
Common Issues
The image below shows step 5 of the Graphical Installation of Anaconda from earlier in this tutorial. Notice that when you install Anaconda, it modifies your .bash_profile to put Anaconda in your path.
The problem is that sometimes people have installed multiple different versions of Anaconda and consequently they have multiple versions of Anaconda in their path. For example, say a person needs Python 2 and they install a Python 2 version of Anaconda, That same person then finds that they need Python 3, so they install a Python 3 version of Anaconda. The problem is that you really only need 1 version of Anaconda. A lot of people think that is that if you install a Python 2 version of Anaconda, you are stuck with Python 2. Anaconda is also an environment manager and makes it very easy to go back and forth between Python 2 and 3 on a single installation of Anaconda (learn more here).
To see if you have more than 1 version of anaconda installed and to fix it if you do, let’s first look at your .bash_profile.
1 - Open a new terminal and go to your home directory. You can do this by using the command below.
2 - Use the cat command to see the contents of the hidden file .bash_profile. Type the following command into your terminal.
You should only see one anaconda version added to your path as you see below, this isn’t a problem for you. Move to the conclusion of the tutorial.
If you see more than one Anaconda version, proceed to step 3.
3 - To remove the old version of Anaconda from your .bash_profile use the command below to edit the file using the nano editor.
From the image above, notice there is a newer Version of Anaconda. Simply remove the older version of Anaconda. Type control + X to exit out of nano.
Save changes by typing Y.
Close that terminal and open a new one. You should be okay now. Keep in mind that this isn’t the only issue you can have when installing Anaconda, but it is a very common issue.
Conclusion
This tutorial provided a quick guide to install Anaconda on Mac as well as dealing with a common installation issue. A graphical install of Anaconda isn’t the only way to install Anaconda as you can Install Anaconda by a Command Line Installer, but it is the easiest. If you aren’t sure what to do after installing Anaconda, here are a few things you can do:
- If you would like to learn more about Anaconda, you can learn about more here.
- If you want to start coding on your local computer, you can check out the the Jupyter Notebook Definitive Guide to learn how to code in Jupyter Notebooks.
- If you want to learn Python, you can check out DataCamp's Intro to Python for Data Science course.
If you any questions or thoughts on the tutorial, feel free to reach out in the comments below or through Twitter.
Download Python | Python.org
Getting started with JupyterLab
The installation guide contains more detailed instructions
Install with conda
If you use conda, you can install it with:
Install with pip
If you use pip, you can install it with:
If installing using pip install --user, you must add the user-level bin directory to your PATH environment variable in order to launch jupyter lab. If you are using a Unix derivative (FreeBSD, GNU / Linux, OS X), you can achieve this by using export PATH='$HOME/.local/bin:$PATH' command.

Run JupyterLab
Once installed, launch JupyterLab with:
Getting started with the classic Jupyter Notebook
conda
We recommend installing the classic Jupyter Notebook using the conda package manager. Either the miniconda or the miniforge conda distributions include a minimal conda installation.
Then you can install the notebook with:
pip
If you use pip, you can install it with:
Anaconda Download For Mac
Congratulations, you have installed Jupyter Notebook! To run the notebook, run the following command at the Terminal (Mac/Linux) or Command Prompt (Windows):
See Running the Notebook for more details.
Getting started with Voilà
See Full List On Docs.anaconda.com
Installation
Voilà can be installed using conda or pip. For more detailed instructions, consult the installation guide.
conda
If you use conda, you can install it with:
pip
Python Anaconda Download Windows 10
If you use pip, you can install it with:
